![]()
Are you having a problem with the search function in the Windows Start menu or File Explorer 10? Whether Windows Can't Find Your Files, indexing is using too much CPU or search is not working, Microsoft's Indexer Diagnostics Tool can help fix the problem.
This tool provides information about the inner workings of the Windows Search Indexer service and can help you identify problems and solutions. It is equivalent to the Diagnostic Data Viewer, a power user tool that provides additional information that you cannot regularly see about Windows internals 10.
To start, download Microsoft Indexer Diagnostic Tool de Microsoft Store. Run it and give it admin access; you need those permissions to enter and update the Windows search indexer.
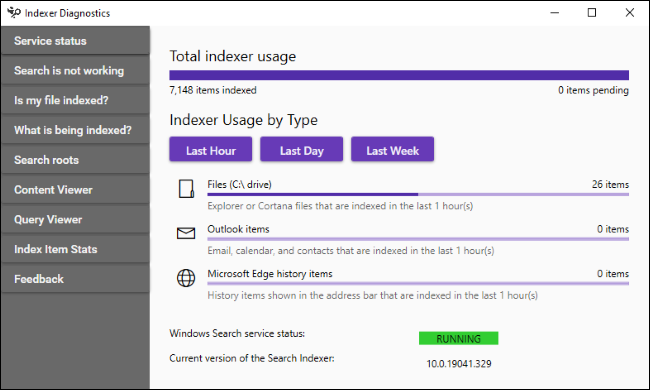
Click between the tabs in the left panel to view information about the indexing service, your state, what files are you indexing and what are you looking for. In addition there are several troubleshooting tools in this panel. The main panel is “Service Status”, which will show you how many items the indexer has in its database and how many files it has indexed in the last hour, day and week.

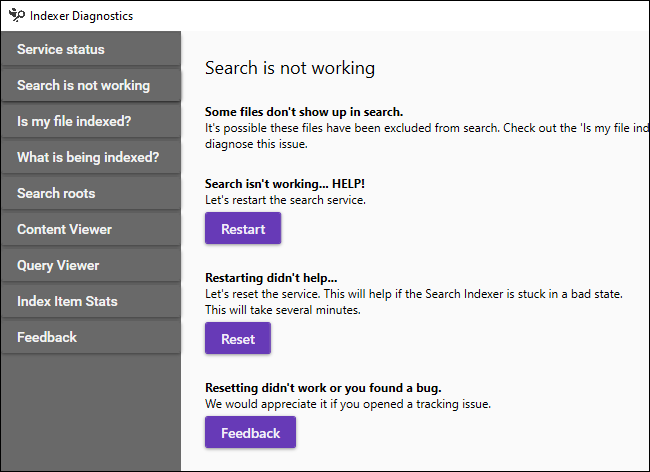
If Windows search doesn't work at all, click on “Search doesn't work” in the left panel. Use the “Restart” to quickly restart the search service and fix problems.
If that doesn't help, Click the button “Restore” to reset the state of the indexing service. This will take several minutes. As the interface points out, a restart “will help if the search indexer is stuck in a bad state”.

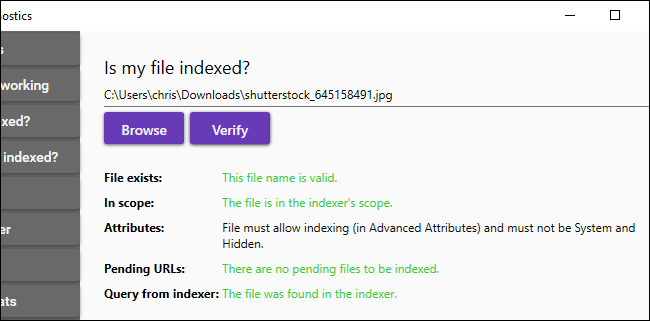
If the search cannot find a file, click on “Is my file indexed?”, Locate the file that you want Windows to find and click “To check”.
Windows will tell you if the file is in the search index and, otherwise, it will explain why the search indexer ignores it so that you can fix any issues.

Other tools available in Indexer Diagnostics include:
- What is indexed? – Shows routes that are being indexed and excluded routes that are not being indexed. You can add and delete included and excluded routes here.
- Search roots – Shows where Windows will start searching, as an example, at the root of the C directory: .
- Content viewer – View the files the indexer indexes and the exact time it indexed them. As an example, if the search indexer was using a large amount of CPU at a specific time, you can see which files you were indexing at the time and consider excluding them from “What is indexed?”.
- Query viewer – Monitor which search queries are sent to the Windows search indexer. You can click on “Start listening”, search and see exactly what's going on in the background.
- Index item statistics – See how many items are indexed by each application on your system. You can also export details about the index to a CSV file.
- Feedback – This tab enables you to compile traces and logs that will monitor resource usage and indexer functions. Here's a button “Error file” that will allow you to report on problems with the indexer with Microsoft.
Many of these features are only useful for developers who work in the search indexer or for people who submit bug reports to those developers., but it's still great to have so much information about the internals of Windows 10.
Microsoft has addressed resource usage issues with the indexer (look at the fixes made in the May update 2020 Windows 10) and this tool suggests that Microsoft developers are working hard to get the most out of the search feature, reduce resource usage and fix bugs.
RELATED: How to find all the files on your PC in the Windows start menu 10