The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) allows you to run Linux software on your Windows PC 11. When you enable WSL, Windows will install a custom Linux kernel. You can then install Ubuntu or another Linux distribution of your choice.
How WSL works on Windows 11
You can enable the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) in all editions of Windows 11, including Windows 11 Home. (You can also install WSL on Windows 10.)
Like the latest versions of Windows 10, Windows 11 usa WSL 2. This second version was redesigned and runs a full Linux kernel on a Hyper-V hypervisor for better compatibility.. When you enable the function, Windows 11 download a Linux kernel created by Microsoft that runs in the background. Windows Update keeps the kernel up-to-date. (You can also use your own custom Linux kernel if you prefer).
To use WSL, you will need to install a Linux distribution. By default, WSL install Ubuntu. This will give you access to a full Ubuntu command line environment using the Bash shell or any other command line shell of your choice.
You can also access your Linux shell environments in the Windows Terminal application included with Windows 11.
You can also run graphical Linux applications out of the box (just install them in linux command line environment and run the command). Windows 11 also includes support for running Linux applications with GPU access, what makes GPU accelerated Linux computing workloads work well on Windows.
The fast way: install WSL with one command
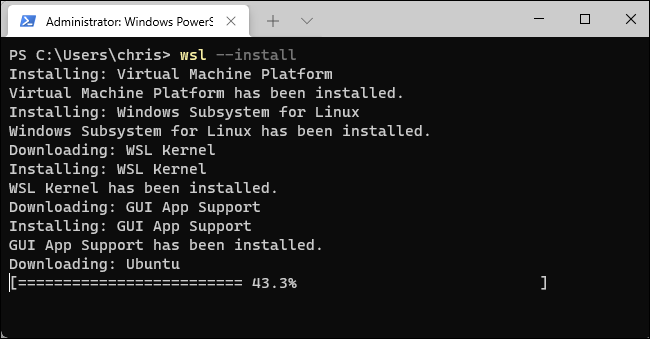
Microsoft has made this process extremely simple on Windows 11. You can enable the Windows Subsystem for Linux and install a Linux distribution like Ubuntu with a single command.
To do this, you will need to use a command line window with administrator permissions. We will do this with the Windows Terminal, although you can also start Command Prompt.
To start a Windows Terminal with administrator permissions, right-click the Start button on the taskbar or press Windows + X and click “Windows Terminal (Admin)”. (You can also find the Windows Terminal shortcut in the Start menu; right-click and select “Execute as an administrator”). Accept the User Account Control message that appears.

To enable the Windows subsystem for Linux and install Ubuntu, what is the default distribution, just run the following command:
wsl --install
When the process is complete, Windows will ask you to restart your PC. Restart your computer. You will be able to use your Linux system after doing so. (You can right-click the Start menu and click Shut Down or Log Out> Reboot to quickly reboot).

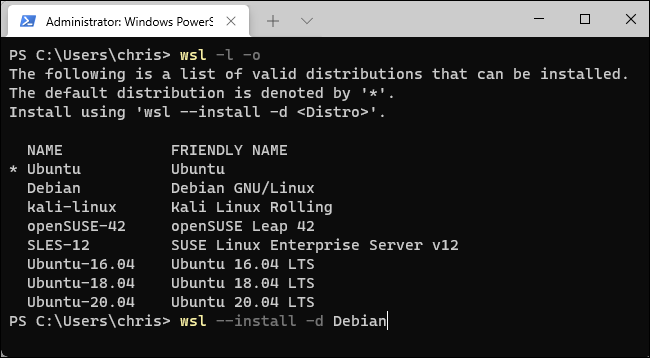
To list other available Linux distributions, run the following command instead. This lists (-l) distributions that are available online (-O).
wsl -l -o
You can install a Linux distribution of your choice by running the following command, replacing “Name” with the name of the Linux distribution, as shown in column “Name”:
wsl --install -d Name
For instance, to install Debian instead of Ubuntu, would execute:
wsl --install -d Debian
You can also run this command multiple times to install multiple Linux distributions on your system.

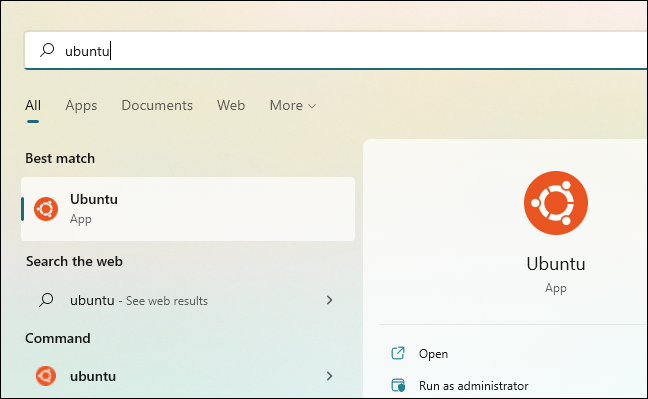
Once your computer has restarted, you can start the Linux distribution you installed from your Start menu.

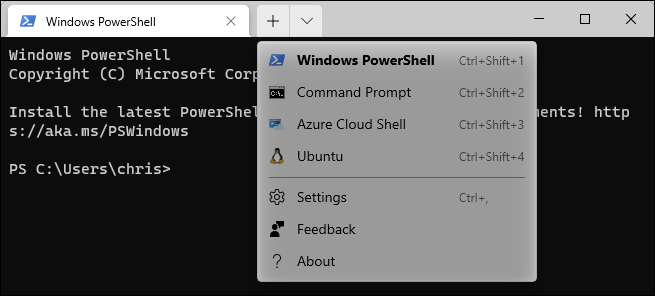
You will also find it as an option in the Windows Terminal application. Click the down arrow to the right of the button “+” from the new tab on the tab bar and select the Linux distribution you installed.
Tip: If you don't see the Linux distribution you installed in the Windows Terminal, start it first from your Start menu. Once you complete your first run setup process, will appear here.

Now, you can use the Linux shell as if you were sitting in front of a Linux PC, or as if you were remotely connected to a server running Linux. You only need to know the Linux commands.
The slow way: enable WSL and install a distribution
You can also enable the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) in the above way. This requires more clicks and we recommend running the above command.
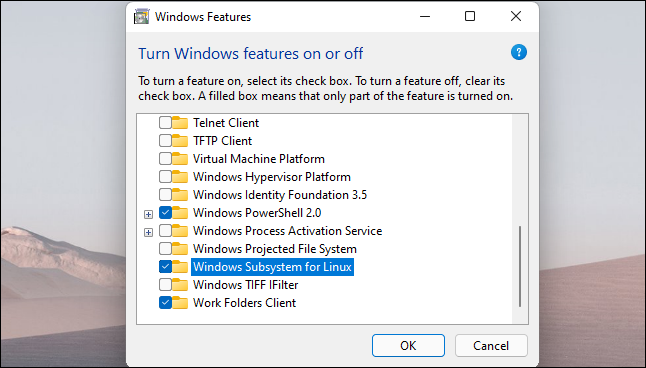
To do this, open your start menu and search “Windows features”. (You can press the Windows key to open the Start menu and just start typing). Launch the shortcut “Enable or disable Windows features”.
Check the checkbox “Windows Subsystem for Linux” here and click “To accept”. You will be asked to restart your computer.

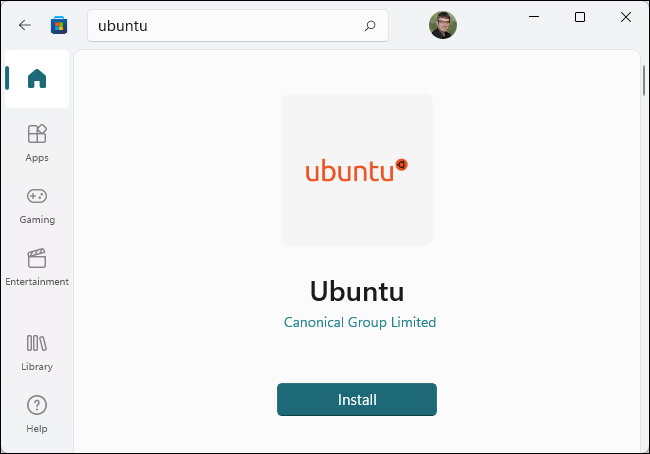
After doing it, open the Microsoft Store app and find the Linux distribution you want to use. For instance, you can search “Ubuntu”.
Install the Linux distribution you want to use (like Ubuntu) as you would with any other application. Just click the button “Install” on your store page.
Now you can start it from your Start menu as if it was installed from the above command.

setTimeout(function(){
!function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s)
{if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function(){n.callMethod?
n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments)};
if(!f._fbq)f._fbq = n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version=’2.0′;
n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0;
t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0];
s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s) } (window, document,’script’,
‘https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js’);
fbq(‘init’, ‘335401813750447’);
fbq(‘track’, ‘PageView’);
},3000);